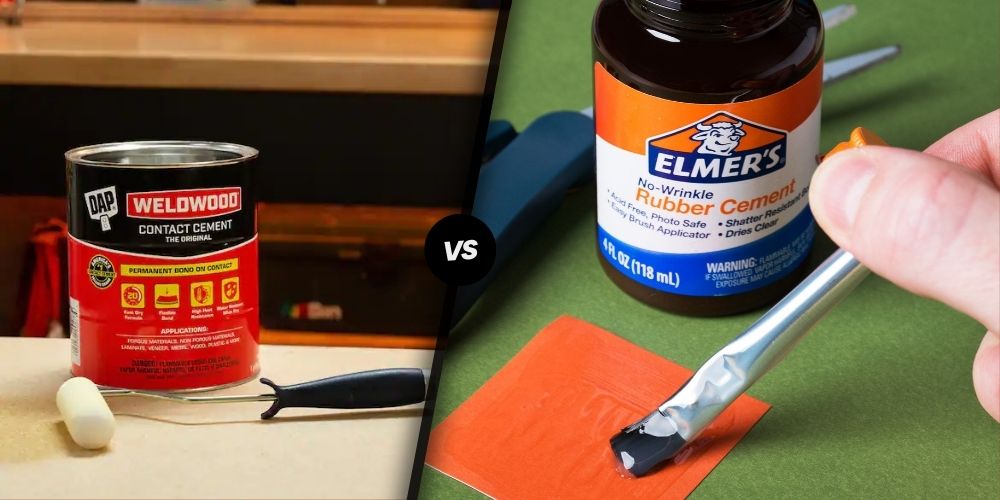
Contact Cement vs. Rubber Cement: Best Uses
Understanding Contact Cement
Contact cement is a versatile adhesive known for its quick-bonding and strong-holding properties. It is widely used in various industries and applications due to its ability to bond a wide range of materials securely.
Characteristics of Contact Cement
Contact cement, when coated on two mating surfaces and allowed to dry, provides an instant permanent bond when brought into firm contact (Quora). This feature makes it almost a general-purpose cement suitable for heavy-duty applications. Key characteristics of contact cement include:
- Instant Bond: Once the two coated surfaces make contact, they form an immediate and strong bond that cannot be repositioned.
- Flexibility: The adhesive remains flexible even after curing, making it suitable for materials that experience movement or stress.
- Water and Heat Resistance: Contact cement is resistant to water and heat, ensuring a durable bond in various environmental conditions.
- Versatility: It can be used on most materials, including wood, metal, glass, rubber, and laminates (Lifehacker).
Best Applications for Contact Cement
Given its strong bonding capabilities and versatility, contact cement is ideal for several specific applications:
| Application Example | Description |
|---|---|
| Adhering Vinyl Flooring | Provides a secure bond for vinyl flooring installations. |
| Metal-to-Metal Bonding | Strong adhesive properties make it suitable for metal repairs and projects. |
| Reattaching Tiles | Ideal for securing loose tiles in flooring or walls. |
| Sealing Leaks | Can be used to seal minor leaks in various materials. |
| Bonding Veneer/Laminate to Wood | Perfect for furniture making and repairs involving veneer or laminate. |
| Minor Shoe Repairs | Can be used to mend shoes by adhering soles and other parts. |
| Leather-Working | Suitable for bonding leather pieces in crafting projects. |
| Attaching Upholstery and Trim in Car Interiors | Ensures a secure bond for car interior materials. |
| Adhering Countertops to Base Cabinets | Reliable for kitchen or bathroom countertop installations. |
Contact cement is recommended over other adhesives in circumstances requiring a strong, water-resistant, and heat-resistant bond. Its immediate bonding and durability make it a favorite for professionals and DIY enthusiasts alike.
For those wondering about other adhesives, check out our comparisons like loctite 510 vs. 515 and contact cement vs gorilla glue.
Exploring Rubber Cement
Rubber cement is a versatile adhesive that offers unique properties suited for various applications. In this section, we will delve into the features of rubber cement and its ideal uses.
Features of Rubber Cement
Rubber cement is known for its flexibility and tackiness even after drying, which makes it suitable for temporary bonding or repositioning needs. Here are some key features of rubber cement:
- Flexibility: Rubber cement remains pliable, allowing for minor movement between bonded pieces. This property is beneficial where slight adjustments are needed.
- Temporary Bond: Rubber cement can be pulled apart easily, making it ideal for temporary applications. However, in some cases, it can become permanent after 48 hours (Fine Leatherworking).
- Tackiness: The adhesive offers a sticky consistency that aids in repositioning items whenever necessary.
Ideal Uses for Rubber Cement
Rubber cement is suitable for a range of purposes due to its unique characteristics. It is commonly used in arts and crafts, school projects, and DIY tasks (Island Chemicals). Its ability to bond different materials makes it a versatile choice for various applications:
| Application | Description |
|---|---|
| Arts and Crafts | Perfect for projects involving paper, cardboard, and other lightweight materials. |
| School Projects | Ideal for quick and temporary bonds needed in school assignments. |
| DIY Tasks | Suitable for home repairs and minor furniture fixes, such as bonding wooden pieces. |
| Leather and Rubber Items | Commonly used to repair leather and rubber items due to its flexible nature. |
| Bag Making | Effective for temporary applications, such as attaching pieces in bag manufacturing. |
For tasks requiring a permanent bond, consider exploring other adhesives. Additionally, always handle rubber cement in a well-ventilated area and avoid using it near flames. Use personal protective equipment like gloves, masks, and goggles (Island Chemicals) to ensure safety.
For more insights on adhesives and their applications, you might find our comparison articles useful, such as barge cement vs. contact cement, liquid nails vs. pl premium, and contact cement vs. rubber cement.
Differences Between Contact Cement and Rubber Cement
Understanding the distinctions between contact cement and rubber cement can help determine the best adhesive for various applications. Factors such as materials used, bonding strength, and flexibility play crucial roles in their differing uses.
Materials Used
Contact cement and rubber cement are both adhesives but are made from different compositions and are suitable for different surfaces (Island Chemicals).
| Adhesive Type | Primary Materials | Characteristics |
|---|---|---|
| Contact Cement | Neoprene, Synthetic rubber | Strong, permanent bond, hardens upon curing (Quora) |
| Rubber Cement | Natural rubber, Solvents | Flexible, easy to apply, remains pliable (Island Chemicals) |
Contact cement is often composed of neoprene and synthetic rubber, making it ideal for providing a strong and permanent bond. Once the coated surfaces come in contact, the bond is instant and irreversible.
In contrast, rubber cement comprises natural rubber dissolved in a solvent, resulting in a more pliable and flexible adhesive. Its flexibility makes it suitable for applications where minor movement of the bonded parts is expected.
Bonding Strength and Flexibility
The bonding strength and flexibility of contact cement and rubber cement differ due to their compositions and curing processes. Knowing these differences can help you choose the right adhesive for your project.
| Adhesive Type | Bonding Strength | Flexibility |
|---|---|---|
| Contact Cement | High, Permanent | Low, Rigid (Quora) |
| Rubber Cement | Moderate, Temporary | High, Pliable (Island Chemicals) |
Contact cement provides a high bonding strength, making it ideal for applications that require a permanent and robust connection. Commonly used in bonding decorative laminates to substrates, once contact is made between the surfaces coated with contact cement, they cannot be moved, highlighting its unforgiving nature (Quora).
Rubber cement, in contrast, has moderate bonding strength and remains pliable even after curing. This characteristic makes rubber cement suitable for applications where flexibility is crucial, such as mounting artwork or temporary bonds where movement is expected (Island Chemicals).
Both adhesives have their distinct advantages and drawbacks. By understanding the differences in materials used and bonding properties, you can select the appropriate adhesive for your specific needs. For more information on related adhesives, explore liquid nails vs. pl premium, loctite 510 vs. 515, or 3m 4200 vs. 5200.
Choosing the Right Adhesive
Selecting the appropriate adhesive for your project is crucial to achieving the best results. When comparing contact cement vs. rubber cement, several factors and application techniques must be considered.
Factors to Consider
- Material Compatibility
- Contact Cement: Suitable for most materials including vinyl flooring, metal, tiles, veneer, laminate, leather, and wood. Offers a permanent, water-resistant, and heat-resistant bond.
- Rubber Cement: Ideal for delicate materials such as paper, foil, fabric, and minor household repairs. Provides a strong yet flexible bond that can be semi-permanent or temporary.
- Bonding Strength and Flexibility
- Contact Cement: Creates a strong, permanent bond that is immediately effective upon drying and is flexible to withstand heat and water exposure (Fine Leatherworking).
- Rubber Cement: Provides a bond that is strong and flexible but can be temporary, allowing parts to be re-arranged easily. Some variants become permanent after 48 hours.
- Application Techniques
- Contact Cement: Requires application on both surfaces and must be allowed to dry completely before bonding the surfaces together. Offers an instant, permanent bond upon contact.
- Rubber Cement: Can be applied to one or both surfaces with options for temporary or permanent bonds. Allows repositioning of materials before the bond sets firmly.
| Factor | Contact Cement | Rubber Cement |
|---|---|---|
| Material Compatibility | Most materials: vinyl, tiles, veneer, wood, metal | Delicate materials: paper, foil, fabric |
| Bonding Strength | Permanent, strong, heat, and water-resistant | Strong, flexible, temporary or semi-permanent |
| Application Technique | Apply to both surfaces, dry before bonding | Apply to one or both surfaces, allows repositioning |
Application Techniques
Applying adhesives correctly ensures the longevity and performance of the bond. The techniques vary depending on whether you are using contact cement or rubber cement.
- Contact Cement Application:
- Clean and dry both surfaces thoroughly.
- Apply an even layer of adhesive to both surfaces.
- Allow the adhesive to dry completely. It typically takes about 15 minutes.
- Once dry, align the surfaces carefully and press them together firmly. The bond is immediate and permanent.
- Rubber Cement Application:
- Clean and dry the surfaces to be bonded.
- Apply a thin, even coat to one or both surfaces.
- For a permanent bond, let the adhesive dry slightly before pressing the surfaces together.
- For a temporary bond, allow one surface to dry completely while the other remains tacky, then press together.
- Repositioning is possible if needed, making it ideal for delicate or flexible materials.
For more information on choosing the best adhesive, you may explore articles like loctite 510 vs. 515, 3m 08693 vs. 08609, and tacky glue vs. hot glue.
Selecting between contact cement vs. rubber cement involves understanding the specific needs of your project. Whether it’s a permanent, robust bond or a flexible, semi-permanent solution, knowing the characteristics and application techniques of each adhesive will guide you to the right choice.
Safety Precautions and Handling
When working with adhesives like contact cement and rubber cement, it is essential to follow proper safety measures to ensure a safe and effective application process.
Ventilation and Flammability
Both contact and rubber cement are known for being highly flammable. Therefore, it is critical to use these adhesives in a well-ventilated area. Proper ventilation helps disperse potentially harmful fumes and reduces the risk of fire or explosion.
According to Island Chemical Paints, rubber cement should be handled away from any open flames or sources of ignition due to its high flammability. The same applies to contact cement. Working in an area with good airflow ensures that the fumes do not accumulate, making the work environment safer.
| Adhesive Type | Flammability | Ideal Ventilation |
|---|---|---|
| Contact Cement | High | Well-ventilated |
| Rubber Cement | High | Well-ventilated |
Personal Protective Equipment
Personal protective equipment (PPE) is crucial when handling these adhesives to avoid exposure to harmful chemicals and reduce the risk of injury. Essential PPE includes:
- Gloves: Prevents skin contact with the adhesive, which can cause irritation or allergic reactions.
- Masks: Protects from inhaling harmful fumes, which can be particularly important in less-ventilated areas.
- Goggles: Shields the eyes from splashes, which could cause severe irritation or damage.
Island Chemicals emphasizes the importance of wearing gloves, masks, and goggles when applying rubber cement. The same protective measures are recommended for contact cement to ensure safety.
| PPE | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Gloves | Protects skin |
| Masks | Protects lungs |
| Goggles | Protects eyes |
For more information on proper safety techniques, readers can explore articles such as application techniques for adhesives and appropriate PPE for glue handling.
By adhering to these safety precautions, users can effectively mitigate the risks associated with using contact and rubber cement, ensuring a safer working environment. Proper handling, ventilation, and personal protective equipment are key components in the responsible use of these adhesives.
Proper Storage and Disposal
Proper storage and disposal of adhesives like contact cement and rubber cement are essential for safety and environmental protection.
Drying and Cleaning Up
When using rubber cement, allow it to fully dry before cleaning up any excess. This drying process ensures that the adhesive sets properly and minimizes the risk of accidental exposure or contact. Ensure the workspace is well-ventilated to disperse any fumes generated during this process.
For cleaning up contact cement, use appropriate solvents designed for the type of adhesive being used. Be sure to follow the manufacturer’s instructions for the correct solvent and procedures. Always wear personal protective equipment (PPE), such as gloves and safety goggles, to protect against chemical exposure.
Storage and Environmental Impact
Proper storage extends the lifespan and effectiveness of both contact cement and rubber cement. Store these adhesives in tightly sealed containers to prevent them from drying out or reacting with air. Keep the containers in a cool, dry place away from direct sunlight and sources of heat or flame. Both types of adhesives are flammable, making it critical to avoid storing them near open flames or high-temperature areas.
| Type of Cement | Storage Condition | Shelf Life |
|---|---|---|
| Contact Cement | Cool, Dry, Airtight | ~1 year |
| Rubber Cement | Cool, Dry, Airtight | ~6 months |
The disposal of these adhesives should follow local regulations. For rubber cement, allow excess to dry completely before sealing the container for disposal. Do not pour liquid adhesives down the drain or into the sewage system as this can cause environmental damage and clogging (Island Chemical Paints).
To learn more about how different adhesives affect the environment, refer to our articles on liquid nails vs. pl premium and jb weld clearweld vs. original.